We have moved to a new server!
Since March 2014, this website has been moved to this new server: http://web.ntnu.edu.tw/~treehopper/. This page will not be updated anymore. Please update your browser’s bookmark or the web links.
Member list
Current members
- Jo-Fan Wang
- 1. The Territorial Behavior of Euphaea formosa (Odonata). 2. Tempo and Mode of Pronotal Evolution in Membracis Treehoppers.
- Hung-Nien Chen
- 1. The effect of typhoon on survivalship of Matrona cyanoptera. 2. Modes of phenotypic variation in Euphaea amphicyana.
- Lan-Wai Yeh
- Ecology and evolution of Taiwanese Carabus ground beetles.
- Yun-Chieh Cheng
- What do damselfly larvae eat? DNA barcode analyses of larval diet in Matrona cyanoptera and Euphaea formosa.
- Chung-Hsin Huang
- Flucuating Asymmetry and Developmental Asymmetry of Cyclommatus mniszechi.
- Hui-Yun Tseng
- 1. Biological function of coloration in Pachyrrhynchus tobafolius. 2. Phylogeny and color evolution of Pachyrrhynchus weevils. 3. Population genetics of Pachyrrhynchus weevils on Lanyu and Green Island.
- I-Ting Hsiao
- Variation of genitalia in Euphaea amphicyana.
- Yen-Ting Chen
- The effect of forest management of Mt. Da-Shiue on the morphological variation of a ground beetle, Carabus (Apotomopterus) masuzoi.
- Jyun-Huei Huang
- The fighting behavior of a stag beetle, Rhaetulus crenatus.
- Shi-Ting Wu
- Membracis Phyllotropis.
- Chiao-Wei Lin
- The fighting behavior of a stag beetle, Rhaetulus crenatus.
- Yong-Chao Su
- Behavioral ecology, sociobiology, population genetics, and molecular phylogenetics.
Past members
- Wei-Liang Xiao
- Variation of wing veins in Euphaea amphicyana.
- Li-Wen Weng
- Why do firefly larvae emit light?
- Yat-Hung Lee
- Speciation of Euphaea damselflies.
- Che-Yu Kuan
- Variation of mandibles in stag beetles.
- Chu-Yen Cheng
- Phylogeography of a Philippine's treehopper, Leptocentrus reponens.
- Ming-Yu Chen
- Phylogeography and population history of the treehoppers, Centrochares horifficus from the Philippines Archipelago.
- Shao-Chang Huang
- Visual Communication of Matrona cyanoptera
- Jen-Pan Huang
- Wei-Yun Chen
- Molecular and Phylogenetic Characterization of Endosymbiotic Bacteria of the Froghopper, Okiscarta uchidae (Insecta: Hemiptera: Cercopidae)
Visiting scholars and students
- Vanitha Williams
- Predatory potential of waterbug, Diplonychus rusticus and dragonfly, Diplacodes trivialis on mosquito larvae.
- Marina Vilenica
- Dragonfly composition (Insecta, Odonata) in wetland area of Turopolje region, Croatia
- Klaas-Douwe 'KD' B. Dijkstra
- History, diversity and identification of dragonflies and damselflies (Odonata).
- Erin McCullough
- " Diversification of weapon form: aerodynamic costs of beetle horns.
- Ashley E. King
- Intrasexual combat and intersexual antagonistic co-evolution in horned beetles.
Jen-Pan Huang

Title
Master student 2005-2008
Species: Euphaea formosa

A female (above) & male (below) of the Euphaea formosa.
Project
Population Genetics and Phylogeographic Analyses of Formosan Damselfly, Euphaea Formosa (Insecta: Odonata: Euphaeidae) from Taiwan
Abstrct
E-mail:airbugs@hotmail.com
1. Population Histories and Evolutions of Endemic Insects in Taiwan.
I am interested in population histories of Taiwanese insects, particularly insects with attractive behaviours and bizarre structures. My graduate study was on the contemporary population structure of an endemic Formosan damselfly, Euphaea formosa. Little genetic structuring was revealed by both mitochondrial and nuclear markers, which is concordant with observed substantial dispersal in this species. Two distinct lineages and historical demographic expansions were inferred using coalescent simulations. The global climate fluctuations during Late Pleistocene were likely responsible for the historical multiple introductions and demographic expansions of the Formosan damselfly through alteration of continental connections and changes of favorite habitats.
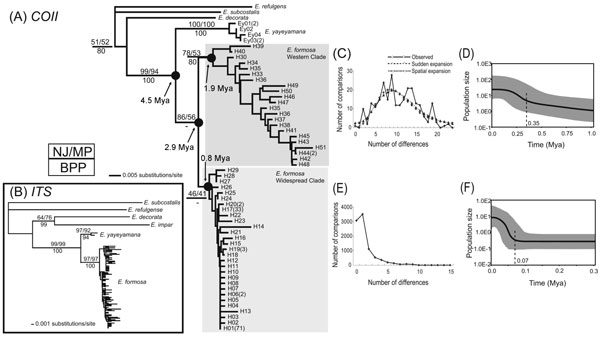
Phylogenies and inferred demographic histories of Euphaea formosa.
2. Genetic and Morphological Studies of Formosan Stag Beetle, Lucanus formosanus.
We also conducted genetic as well as morphological studies on Formosan stag beetle, Lucanus formosanus, which is traditionally believed to exhibit distinct morphological variations among populations. Despite rampant gene flows among populations around the central mountain range (CMR) were inferred using neutral molecular markers, significant morphological divergence was found among populations. Selections on certain genes (or traits) while the others are allowed to be exchanged among populations is the paradigm of ecological speciation or parapatric speciation, which is currently resurrected. The observed different population densities and co-dwellers could be the driving forces of the morphological divergence in the face of substantial gene flows in the Formosan stag beetle.
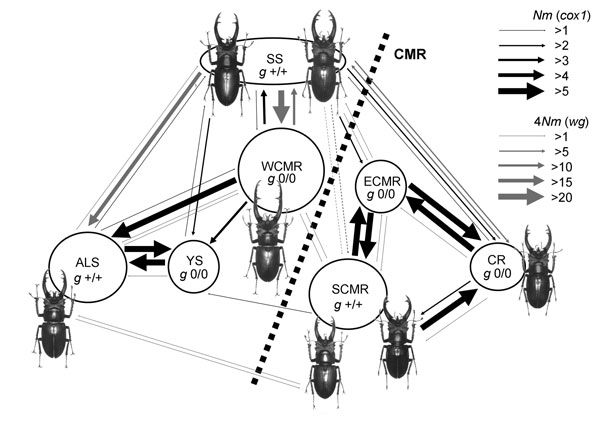
Rampant gene flows and significant morphological differentiations of Lucanus formosanus populations around CMR. Pictures courtesy to Fu-Lin Yang (2008).
Present address
Dr. Lacey Knowles's lab, Museum of Zoology, University of Michigan, 1109 Geddes Avenue, Ann Arbor, MI 48109, USA.
E-mail:huangjp@umich.edu
Publication
Huang, J-P. , and C-P. Lin. 2011. Lineage-specific late Pleistocene expansion of an endemic subtropical gossamer-wing damselfly, Euphaea formosa, in Taiwan. BMC Evolutionary Biology 11:94.
Huang, J-P. , and C-P. Lin. 2010. Diversification in subtropical mountains: Phylogeography, Pleistocene demographic expansion, and evolution of polyphenic mandibles in Taiwanese stag beetle, Lucanus formosanus. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 57: 1149–1161.
Lin, C-P., M-Y. Chen and J-P., Huang. 2010. The complete mitochondrial genome and phylogenomics of a damselfly, Euphaea formosa support a basal Odonata within the Pterygota. Gene. 468: 20–29.
Lin, C-P., J-P. Huang, Y-H. Lee and M-Y. Chen. 2009. Phylogenetic position of a threatened stag beetle, Lucanus datunensis (Coleoptera: Lucanidae) in Taiwan and implications for conservation. Conservation Genetics. 15 Oct 2009, Online First.